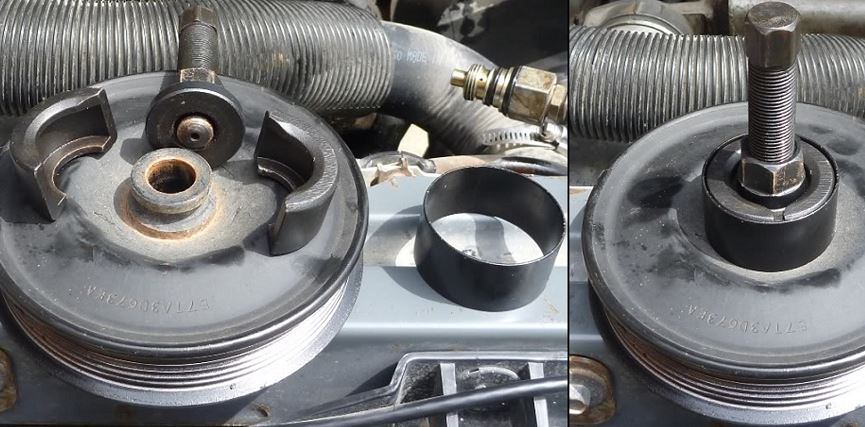
Alternator and timing belts are the two main belts in a vehicle’s engine, responsible for many vital functions. Both belts are alike in color and shape, and it’s common for car owners to mix them up, thinking they are the same. They are not, and perhaps the only thing they have in common is rubber, their base material, which could also be different. They vary remarkably in their locations beneath your vehicle’s hood and the roles they perform also are different. In this article, we’ll cover the unique features of each belt that is the alternator belt vs timing belt,, which will help you to spot their differences and identify them when necessary.

We also are going to address the following questions: Is the alternator belt the same as the timing belt? Can timing belt affect the alternator? What is another name for the timing belt? What are the 3 belts in a car?
What are the signs of a bad alternator belt? What are the signs of a bad timing belt?
alternator belt vs timing belt, comparing the difference. Are you ready?
Let’s get started.
Is the Alternator Belt the Same as a Timing Belt? What’s the Difference?
The answer is no, they are not the same, and here is why.
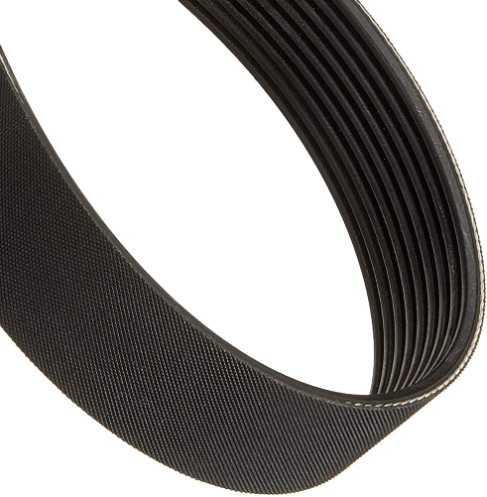
The alternator belt is an oval-shaped rubber belt located outside the engine. The role of this belt is to supply power to the engine’s critical accessories that in turn, lead to the basic functions and luxuries you enjoy in a car. For instance, the alternator belt powers the alternator by rotating it ,which helps to charge your car’s battery and supply power to the electrical components of your car. The alternator belt also powers the radiator, air conditioning compressor, power steering, and water pump when fully functional.
On the contrary, the timing belt looks just like the alternator but is located inside the engine and is responsible for the synergized running of the crankshaft and camshaft. This synergy ensures that the opening and closing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves are in sync with the rapid movements of the pistons, a crucial process in the smooth operation of an engine. This process ensures fuel and air go into the combustion chamber when necessary and allows for the exit of exhaust fumes from the same combustion chamber.
Primarily, the timing belt works within the internal combustion section of an engine to ensure smooth engine operations, whereas the alternator belt works on the exterior of the engine to coordinate smooth operations of other relevant components of the engine like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
How to Spot the Difference Between an Alternator Belt and a Timing Belt?
Since both belts are similar in shape and sometimes rubber material, it can be tricky to tell the difference when both are before you. They have clear differences in design, which is the main distinguishing factor between them, aside from their locations and functions in the engine.
The alternator belt has several vertical V-shaped grooves across its length, while that of a timing belt have teeth, lined horizontally and specially adapted to fit into the cogwheels of the crankshafts and camshafts. Beyond the technical terms of their designs, which might be too complex to grasp, you can basically identify both from the visible lines within the belt – alternator belts are vertical and timing belts are horizonal.
Alternator Belt vs. Timing Belt Differences
| S/N | Alternator Belt | Timing Belt |
| 1 | Located outside the engine | Located inside the engine |
| 2 | Powers essential functions of the vehicle (air conditioning, power steering, battery, electronics) | Ensures the smooth running and combustion process of the vehicle’s engine |
| 3 | All critical components attached to the belt stops working when it fails | A failed timing belt leads to the breakdown of the engine and the entire vehicle |
| 4 | The belt squeals when in bad condition | The belt makes ticking or clicking sounds |
| 5 | Multiple belts can be used to power the different critical components of the vehicle | Only one belt is used to synchronize the crankshaft with the camshaft |
| 6 | Has V-shaped vertical grooves | Has horizontal teeth |
So Can the timing belt affect the alternator?
Can Timing Belt Affect Alternator?
The timing belt ensures the engine runs smoothly and when it fails, it could lead to the total breakdown of the engine, and by extension, the entire vehicle. Since the alternator is part of the engine, the failure of the timing belt will inevitably affect it. However, the failure of an alternator belt won’t affect the entire engine. It will only affect the vital components that depend on it for power. In cases where a vehicle uses different belts for its alternator, power steering, and air conditioning compressor, the failure of the alternator belt only affects the car’s battery by not charging it.
What’s Another Name for a Timing Belt?
The belt is called a timing belt because it regulates the timing of the engine’s valves. Since it’s also responsible for maintaining the synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft, it can also be called Camshaft Belt and sometimes, in rare cases, called a Gilmer belt.
What are the Three Belts in a Car?
The three main belts in the engine of a car are:
- Timing Belt – The belt that ensures synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft inside the engine block.
- Serpentine Belt (Drive Belt) – The belt located outside the engine block that ensures other critical accessories of the vehicle are functional by supplying them with power.
- Alternator Belt – A special belt for the alternator that supplies power to charge the car’s battery.
There are other types of belts, such as fan and power steering belts. These days, vehicles use one belt – a serpentine belt to supply power to the alternator, air conditioning compressor, power steering, and water pump. Eliminating the need for three or four separate belts.
This multipurpose belt system have trimmed the number of belts in a typical modern engine to just two – the serpentine and timing belt. The serpentine is also known as alternator belts as both are used interchangeably to mean the same thing. However, if there’s a separate belt for the engine’s alternator, then it’s called an alternator belt, otherwise, the serpentine belt functions as an alternator belt.
What are the Signs of a Bad Alternator Belt?
There are many signs of a failing alternator belt that shouldn’t be treated lightly. Some of these signs include:
Loud Squeaky and Chirpy Sounds
When you start hearing squeals and chirps beneath the hood of your vehicle, it’s a sign that the alternator belt is damaged, loose, or faulty, especially when the weather isn’t cold.
The Battery’s Warning Light is On
The battery warning light indicates that the battery is low, and that means the alternator hasn’t been functional in charging the car’s battery because of a defective belt.
Dimming Back and Headlights
When your headlights and general car lighting accessories begin to dim or appear in flashes, it’s a sign that the alternator is not fully functional and the car’s battery is getting low.
Dead battery
A dead battery is an obvious indication that the alternator belt has failed after struggling and squealing for attention but lacking any.
Stiff Power Steering
Stiff powering steering is a sign that the alternator powering the steering is not functioning at optimal capacity due to a failing alternator belt.
What are the Signs of a Bad Timing Belt?
When a timing belt is damaged or loose, you can tell from the following signs:
Periodic Clicking Sounds
When you start hearing ticking or clicking sounds from the engine’s interior, something is wrong with the timing belt and it could be wearing out. A worn-out belt will be struggling to live up to its daily expectations in the engine and sounds are a way of indicating this weariness.
Smoke After Starting the Vehicle
When the exhaust dispels fumes more than usual after starting the vehicle, it means the combustion of fuel inside the chamber is incomplete because the timing belt is growing weak. Incomplete combustion leads to high fumes of smoke and soot. A fully functional timing belt ensures the smooth running of the combustion process without smoke.
Slow Starting
When the engine hesitates to start after you’ve turned on the ignition, it may be that the crank and shaft aren’t working effectively, which is the timing belt’s job. When the timing belt eventually breaks, the engine won’t even start.
Oil Leaks
When you start noticing oil spills around the engine’s motor, the timing belt cover may be loose, because the nuts and bolts that hold it in place have grown weak. Hence, it needs tightening.
Conclusion
Alternator belts and timing belts are popular in the auto industry and among car owners who will at one point, deal with either of them. They may appear alike in shape and color but vary significantly in functions, designs, and location beneath the hood of a vehicle. This article has covered all you need to know about Identifying them, especially the signs they display when bad, which is critical to resolving whatever challenges they may have. Consequently, you can prevent the breakdown of your vehicle or its essential components.

Uchenna is a Radiographer and Auto parts mechanic who recently got his automotive diploma as an auto repair technician, and since then, has worked on fixing various car problems.
Working as just a radiographer, Uchenna didn’t just get all the fulfillment he desired, because he truly loved doing things tilted toward cars. As a kid, he would take apart his toy cars to see how they worked and would spend hours tinkering with his bike.
So, in 2017 he made the tough decision to become an auto mechanic. He threw himself into his studies and now loves every aspect of what he does.
He gets to work with his hands, solving problems and bringing cars back to life, and sharing his knowledge and easy quick-fix guide online are all part of what makes him feel fulfilled.




